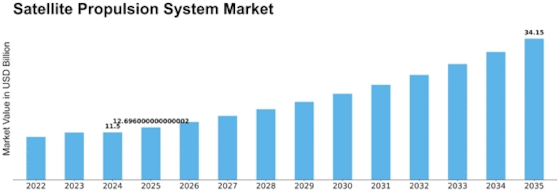
The Satellite Propulsion System Market is becoming increasingly competitive as technological breakthroughs, miniaturization and rising satellite-launch volumes redefine the industry landscape. With the market expected to grow from USD 11.5 billion in 2024 to USD 34.15 billion by 2035 (MRFR), companies across the propulsion ecosystem are adopting new strategies to strengthen their market positions. Competition is no longer driven solely by performance—it now includes cost efficiency, sustainability, manufacturing scale and mission adaptability.
Traditionally, propulsion markets were dominated by large aerospace suppliers delivering chemical or cold-gas propulsion systems. MRFR highlights that cold-gas propulsion still retains a notable share due to its reliability and simplicity. Yet, as new mission requirements emerge—especially in LEO constellations—electric propulsion and hybrid systems are becoming essential competitive differentiators. These technologies offer higher fuel efficiency and better payload-to-mass ratios, making them ideal for long-duration and frequent-maneuver missions.
One strategy reshaping the competitive landscape is vertical integration. Larger aerospace firms increasingly acquire propulsion startups to bring innovation in-house and reduce supply-chain dependency. This mirrors trends in the broader Space Propulsion Systems Market, where consolidation is common as companies seek end-to-end capability. Vertical integration allows firms to offer fully integrated propulsion-plus-power packages—an advantage highly valued by satellite manufacturers.
Another emerging strategy involves scalable manufacturing. With satellite constellations requiring dozens or even hundreds of spacecraft, propulsion systems must be produced quickly, cost-effectively and with consistent quality. Companies are shifting from custom-built thrusters to modular, mass-manufacturable propulsion units. In some ways, this mirrors efficiency improvements seen in the aircraft propulsion system market, where standardization supports global scalability.
Partnerships and collaborations are also central to competitive positioning. Propulsion manufacturers collaborate with satellite designers, launch providers, and even government agencies to co-develop mission-optimized solutions. Joint R&D initiatives help companies stay aligned with future mission needs—from advanced earth-observation to deep-space communications. These collaborations reduce time-to-market and ensure propulsion systems meet evolving orbit-regulation and sustainability requirements.
In addition, propulsion companies are heavily investing in green propulsion and advanced materials. Lightweight composites, eco-friendly propellants and high-efficiency electric architectures are becoming market-winning features. As global interest in sustainable space operations grows, propulsion-system providers that prioritize clean and high-performance technologies will gain competitive advantage.
Regionally, competition varies. North America’s dominance is supported by the presence of major aerospace primes and high R&D spending. Europe’s market is driven by advanced electric propulsion development and strict sustainability objectives. Asia-Pacific companies, meanwhile, focus on affordability, miniaturization and rapid deployment—making the region the fastest-growing according to MRFR.
Looking ahead, the companies that lead the market will be those that combine innovation, adaptability and manufacturing strength. Autonomous orbit-control, AI-driven propulsion management and advanced electric/hybrid systems could define the next generation of competitive propulsion solutions.
Overall, the Satellite Propulsion System Market is shifting from tradition-driven engineering to innovation-driven competition. With strong global demand and expanding mission variety, the next decade will belong to propulsion companies capable of delivering efficient, versatile and scalable solutions tailored for a rapidly evolving space environment.